Glutathione: Benefits, Side Effects, and Dosage
Glutathione is one of the natural components inside the human body, playing an extremely important role in our health. In addition to being produced naturally by the body, glutathione can be given intravenously, as an oral tablet, or as an inhaler.
1. What is Glutathione?
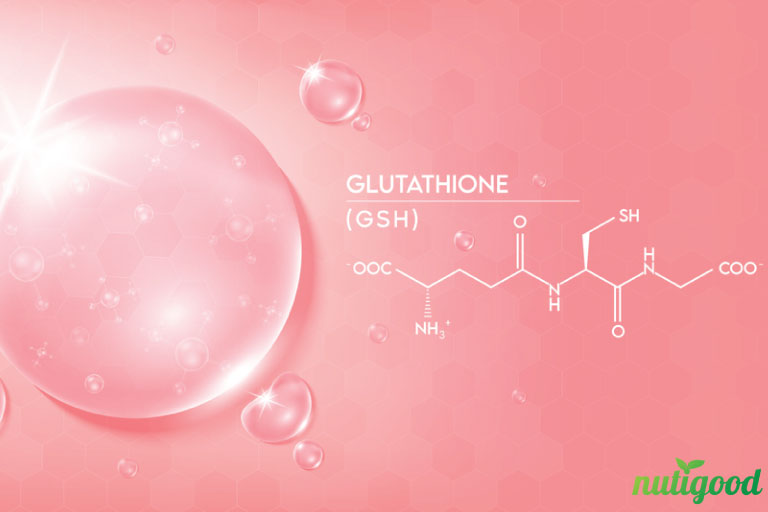
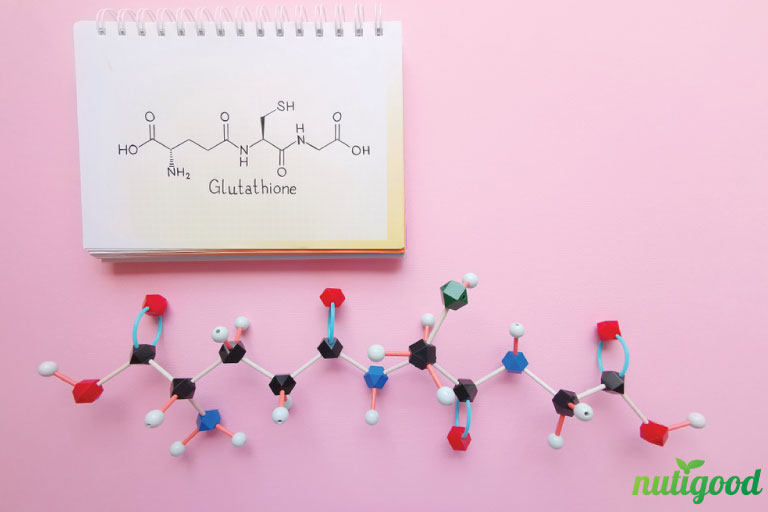
Glutathione (GSH) is a natural substance produced naturally by the liver and found in fruits, vegetables, and meat and synthesized from cells by 3 amino acids: Cysteine, glutamic, and glycine.
Glutathione levels in the body can be impaired by several factors, including poor nutrition, environmental toxins, and stress. In addition, its concentration may also decline gradually with age.
2. Uses of Glutathione
Depending on each use as well as the intended use of the patient, Glutathione brings different uses, namely:
2.1 Using oral Glutathione for treatment
Glaucoma and cataracts
Anti-aging
Treat or prevent alcoholism, asthma, heart disease (atherosclerosis and high cholesterol), cancer, hepatitis, liver disease, diseases that weaken the body’s immune system (including AIDS and chronic fatigue syndrome), dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, osteoarthritis, and Parkinson’s disease.
Maintain a healthy immune system, and prevent the body from being poisoned by metals and drugs.
2.2 Using inhaled glutathione to treat
Lung infections, including cystic fibrosis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and lung disease in people with HIV infection.
2.3 Using Glutathione intravenously for treatment
Infertility in men
Preventing dangerous side effects of cancer treatment (chemotherapy)
Prevention of fatigue and anemia in patients with kidney disease undergoing hemodialysis
Preventing kidney problems after heart surgery
Treatment of Parkinson’s disease
Improves blood flow and reduces blood clotting in people with hardening of the arteries of the liver (atherosclerosis)
Treatment of diabetes
Prevent dangerous side effects of chemotherapy.
3. Glutathione’s Mechanism of Action
Glutathione is involved in many processes in the body, including building and repairing tissues, making chemicals and proteins needed in the body, and the immune system.
Because glutathione is such a powerful antioxidant, every cell in the body needs it to stay healthy. It is considered a magnet to attract free radicals, heavy metals, and toxins that are absorbed every day through the skin, breath, drinking water, and food to stimulate their elimination from the body, and keep the body healthy.
Glutathione is not only produced naturally by the body but can also be recycled. In the absence of glutathione recycling, the body will encounter an overload with toxins which leads to a breakdown of the existing balance.
4. Dosage of Glutathione
Glutathione is available in two dosage forms:
Powder form
Package form.
Glutathione dosage will depend on each person’s purpose, age, health condition, and some other issues. When taking Glutathione to whiten skin will be different from taking Glutathione to prevent and treat diseases. However, it should be noted that oral administration of Glutathione takes a certain amount of time to achieve optimal effectiveness. Therefore, you should be persistent in using it according to the dosage and course prescribed by your doctor.
4.1 Dosage of Glutathione for skin whitening (oral)
For the first 3 months, you can take about 1000mg-2000mg of Glutathione, then reduce to 500 mg per day. Doctors also recommend that you should not take more than 2000 mg of Glutathione per day and should not use them for a long time, because it can cause poisoning and other dangerous complications.

4.2 Dosage of Glutathione to support cancer treatment (oral).
To support the treatment of cancer, patients can supplement with Glutathione to protect the body from the dangerous side effects of chemotherapy. Glutathione can be taken orally before radiation therapy:
Taking 1000mg of Glutathione daily helps protect kidney cells, and nerve cells from the toxic effects of chemotherapy (Oxaliplatin, Cisplatin, Cyclophosphamide, 5. FU,…)
Taking 500-1000 mg/day helps to improve and restore health and prevent exhaustion for cancer patients.
4.3 Dosage of Glutathione to support the treatment of liver disease (oral).
Because Glutathione is effective in restoring liver function, you can supplement about 1000 mg of Glutathione per day to protect liver cells and avoid necrotic damage caused by peroxide free radicals in hepatitis caused by free radicals. poisoned.
In case you have viral hepatitis, you should take about 500mg per day until you recover.
Patients with cirrhosis or liver failure should take 500-1000 mg/day to help the liver remove toxins from the body.
Many other conditions can be treated with the use of Glutathione, including myocardial infarction, diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, HIV, and brain damage from trauma. For each disease, the doctor will prescribe the most appropriate dose of Glutathione.
Read morẻ:

One thought on “Glutathione: Benefits, Side Effects, and Dosage”